In this article, you’ll explore the advanced engineering behind thermal transfer ribbons and their essential role in printing. While they may appear to be simple components, these ribbons are developed using cutting-edge technology. Used widely for label printing across different industries, they undergo a meticulous manufacturing process to ensure superior quality, long-lasting performance, and cost efficiency. Made from wax, resin, or a combination of both, these ribbons work with specialized inks to produce crisp, durable prints. Read on to uncover how they function and what materials make them unique.
Understanding thermal transfer ribbons: How do they work?
Thermal transfer ribbons (TTR) play a critical role in the thermal transfer printing process. They consist of a plastic film with ink on one side and a silicone coating on the other. The silicone layer minimizes friction and prevents overheating during printing, ensuring smooth operation.
As the ribbon moves through the printer and heats up, the ink is released and transferred onto the label or other materials, creating sharp and reliable prints. Depending on the type of ribbon, the coating may include wax, resin, or a blend of both. Wax-based ribbons are excellent for short-term applications, while resin ribbons provide superior durability for long-term usage.
Primary applications of thermal transfer ribbons
Thermal transfer ribbons are widely used in various industries for printing durable labels, barcodes, and tags. The ribbons are heated by the printer’s printhead, melting the ink and transferring it onto the material’s surface. The resulting prints are resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, heat, and abrasion. Industries such as logistics, manufacturing, healthcare, and retail rely on these ribbons for inventory management, product labeling, and compliance requirements.



Thermal transfer vs. direct thermal printing: Key differences
- Thermal Transfer Printing: This method requires a ribbon coated with ink. The printer’s heated printhead transfers the ink onto the label, producing prints resistant to heat, chemicals, and wear. This is the preferred method for long-lasting, high-quality labeling needs.
- Direct Thermal Printing: Unlike thermal transfer printing, this method uses heat-sensitive paper that darkens when exposed to heat. It does not require a ribbon, making it a more cost-effective option. However, the prints are less durable and may fade over time when exposed to light, heat, or friction.
Composition of a thermal transfer ribbon
Thermal transfer ribbons consist of multiple layers that contribute to their efficiency and durability:
- Backcoat: This is a specialized protective coating applied to the back of the ribbon. It serves multiple functions, including reducing friction between the ribbon and the printhead, dissipating heat, and preventing static buildup. By minimizing wear on the printhead, the backcoat significantly extends its lifespan, reducing maintenance costs and ensuring consistent print quality over time.
- Release Layer: This layer acts as an intermediary between the ink and the polyester film, ensuring that the ink releases properly during the printing process. Without a well-designed release layer, ink may not transfer smoothly, leading to smudging, incomplete prints, or excessive wear on the ribbon. It is formulated to allow just the right amount of adhesion so that ink transfers efficiently while preventing unnecessary residue buildup.
- Polyester Film (Carrier): The backbone of the ribbon, this PET (polyethylene terephthalate) film provides the structural integrity needed to hold the ink and other layers in place. Its durability ensures that the ribbon remains stable throughout the printing process, allowing for precise and consistent printing results. A high-quality polyester film is crucial for maintaining smooth movement through the printer and ensuring even ink distribution.
- Ink Layer: The most important functional component of the ribbon, the ink layer contains the pigment that will be transferred onto labels or packaging. Depending on the application, the ink formulation may include:
- Wax: Ideal for printing on paper labels that do not require high durability.
- Resin: Designed for high-resistance printing on synthetic materials that must withstand harsh conditions.
- Wax-Resin Blend: Offers a balance between durability and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for semi-rugged environments.
- Trailer: Positioned at the end of the ribbon, the trailer acts as a sensor that signals the printer when the ribbon is nearly depleted. This prevents the printer from running without ribbon, which could lead to printhead damage. Some advanced trailers also include conductive elements that interact with the printer’s internal mechanisms to automatically halt printing when the ribbon runs out.
- Core: The central support structure around which the ribbon is wound. Cores are typically made from either cardboard or plastic, depending on the manufacturer and ribbon type. A sturdy core ensures smooth unwinding and rewinding during the printing process, preventing ribbon misalignment and potential print defects.
- Leader: This PET (polyester) strip is located at the beginning of the ribbon roll. It serves several purposes, including protecting the ribbon before use, providing identification details about the ribbon composition, and facilitating easy installation into the printer. The leader ensures that users can quickly load the ribbon and align it properly for optimal printing performance.

Types of thermal transfer ribbons and their uses
Thermal transfer ribbons come in different types, each designed for specific printing needs. Choosing the right ribbon is crucial to ensuring high-quality, long-lasting prints suited to the application and environment.
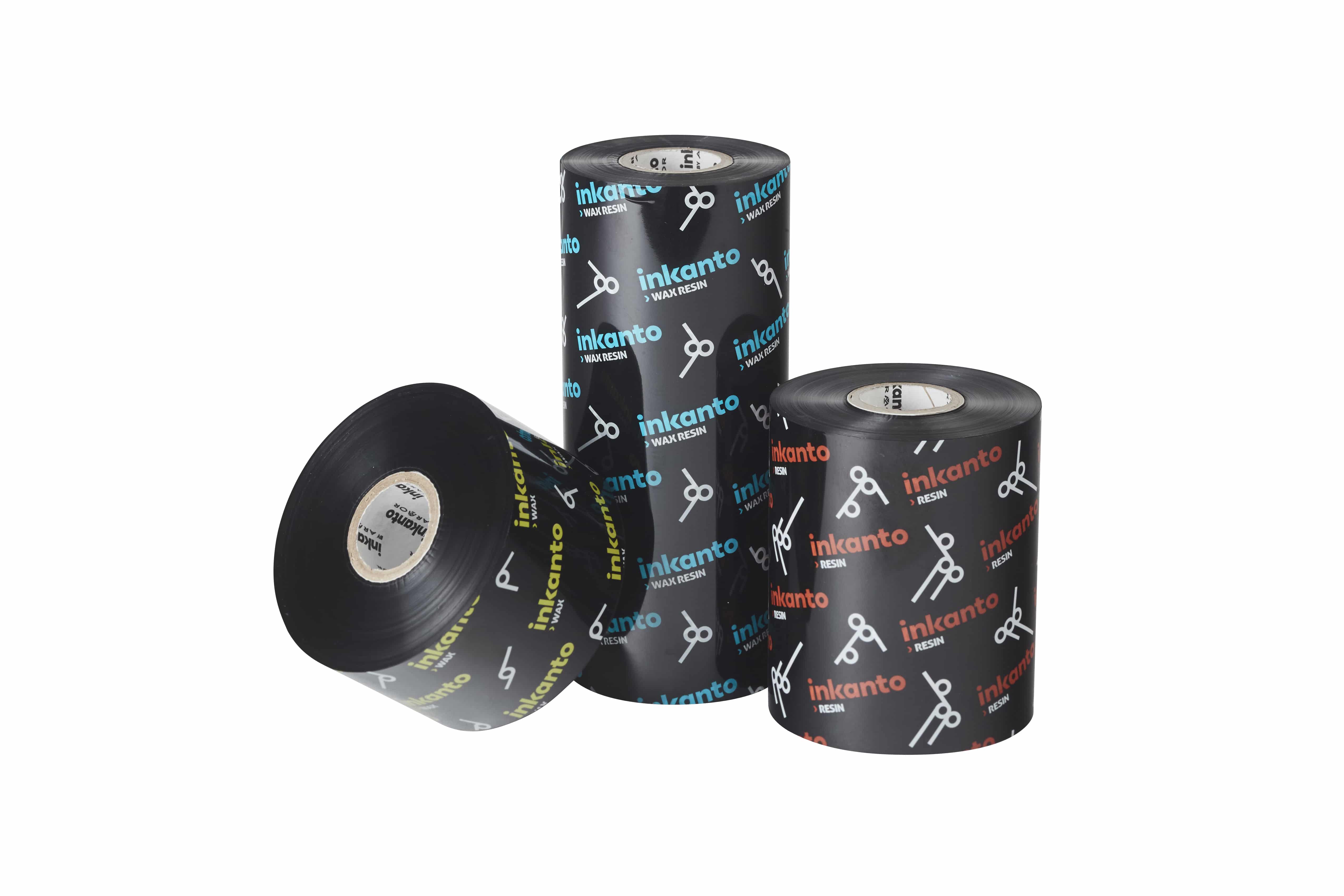

- 1. Wax ribbons – a cost-effective solution for short-term applications
Wax ribbons are the most affordable and widely used option for printing on paper labels. They provide excellent print quality and are ideal for applications where durability is not a primary concern. However, wax prints are more sensitive to friction, moisture, and heat, making them unsuitable for harsh environments. These ribbons are commonly used for logistics, retail labeling, and general inventory tracking, where labels do not need to withstand extreme conditions. - 2. Resin ribbons – maximum durability for extreme conditions
Resin ribbons are the most durable option, designed for applications requiring resistance to chemicals, high temperatures, abrasion, and moisture. The ink adheres strongly to synthetic materials such as polyester, polypropylene, and vinyl, ensuring long-lasting prints that do not fade or smudge. Due to their high resilience, resin ribbons are widely used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, automotive, and laboratories, where label durability is critical. - 3. Wax-resin ribbons – a balanced choice for moderate durability
Wax-resin ribbons offer a compromise between cost and durability, providing higher resistance than pure wax ribbons while being more affordable than resin ribbons. These ribbons are designed for printing on both coated paper and some synthetic materials, offering improved resistance to smudging, moisture, and light handling. They are commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and warehouse management, where labels need to last longer than standard wax prints but do not require extreme durability. - 4. Textile resin ribbons – designed for fabric applications
Textile resin ribbons are specifically developed for printing on fabric labels, ensuring long-lasting readability even after multiple washes. These ribbons are highly resistant to industrial washing, detergents, high temperatures, and ironing. As a result, they are widely used in the textile and apparel industries for clothing labels, care tags, and product branding, where printed information must remain intact despite frequent exposure to water, heat, and chemicals.
By understanding the characteristics and uses of each type of thermal transfer ribbon, businesses can choose the best option for their specific labeling needs, ensuring optimal print quality and longevity.
Thermal transfer ribbons are indispensable for producing high-quality, durable prints across various industries. Understanding the different types—wax, resin, mixed, and textile resin—ensures that you select the right ribbon for your specific printing needs. Whether you require short-term labeling or highly durable prints, there is a thermal transfer ribbon tailored to meet your requirements.
This article is presented by Armor Iimak, a leader in thermal transfer ribbon manufacturing. With extensive expertise in the industry, Armor Iimak offers a diverse range of high-quality solutions for all your printing needs. Contact our team today for expert guidance in selecting the perfect ribbon for your applications.
